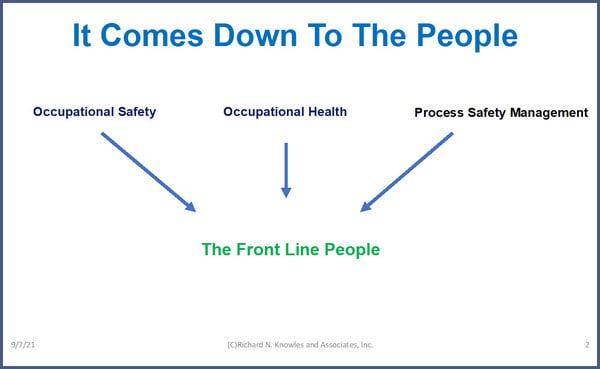
To really improve safety in an organization, the people (all the employees) need to come together and fix the whole system.
This is much more than just a safety issue in an organization. It is a “together” issue.
My Experiences:
Top-Down Organizations
I have been working in various aspects of safety for over 60 years. Almost all the organizations with which I have worked have been top-down managed. This approach has been used by armies, churches, governments, and businesses for centuries. Those in control, at the top, issue the orders and rules, the managers in the middle of the organization are expected to follow and impose these onto the people at the bottom of the organization.
This probably made sense when most of the population was poorly educated and illiterate. But now, here in the USA and other developed countries, this is not the case. Most of the people are fairly intelligent and manage their personal lives quite well. They raise families, buy homes and cars, have complex hobbies, etc. They know how to do a lot of things pretty well.
When these people work in top-down organizations where they are not treated with respect, told what to do, and are pushed around like the interchangeable parts of a machine, they are not usually very happy or productive. Dysfunctional behaviors and troubles like bullying, resistance to change, cutting corners, poor morale and performance, anger, and frustration cause huge losses, like terrible productivity and people quitting.
When safety improvement efforts like bringing in a consultant to fix the safety culture, or to improve safety practices like behavior-based safety, or improve participation are conducted, they often meet a lot of resistance and do not sustain themselves. Most people do not like to be pushed around and treated as if they do not have a brain.
In this environment, it is very difficult to make good safety improvements and very, very hard to sustain the programs. People keep getting hurt and killed.

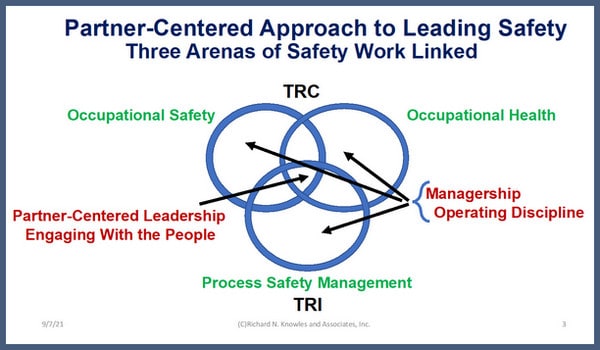
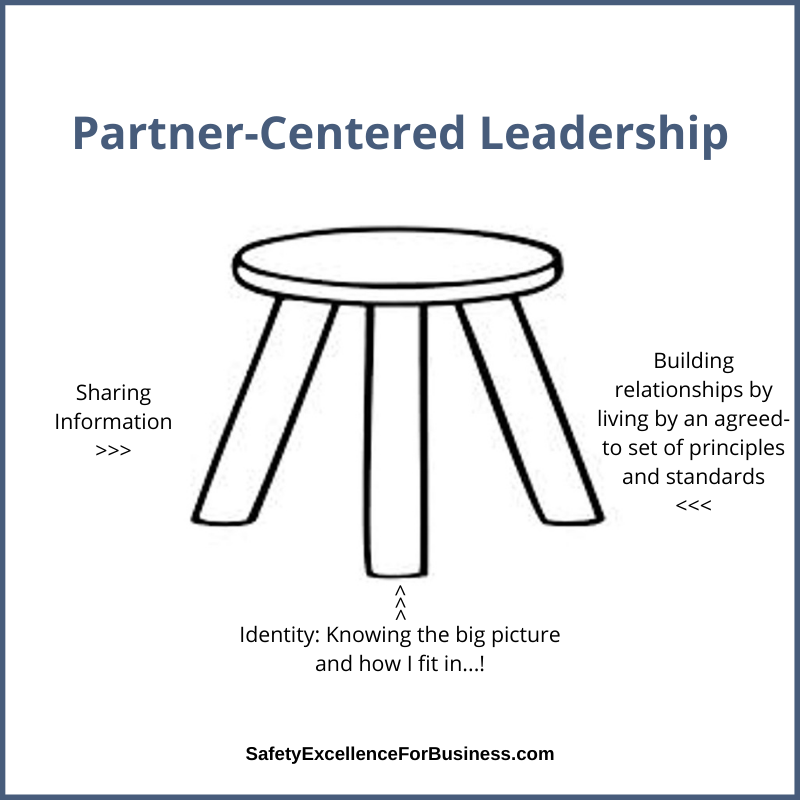
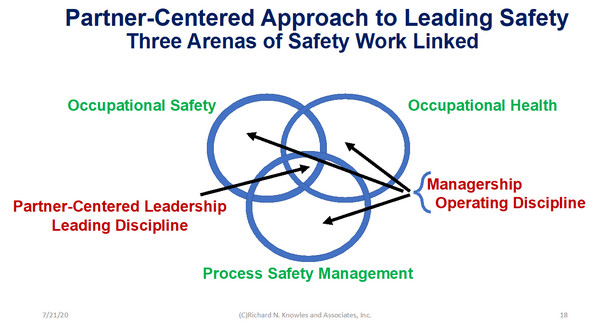
Partner-Centered Leadership
In working in and leading organizations, I have found that people want to be treated with respect, listened to, share ideas, and learn together. These apply to people in all the various parts of the organization, not just safety.
Our Partner-Centered Leadership Workshops include a broad cross-section of people from around the organization and from different levels so that the whole of the organizational system is together for the work. We help people to see their organization as if it is a living system.
As the workshop process develops, the people can see the whole, the parts and the interaction of the parts, which opens-up all sorts of new, creative ideas. Everything is connected to everything else.
As they learn to work together in new ways, they co-create the changes they want to make and a new culture begins to emerge out of the conversations. The whole organization changes and improves, including their safety performance. The improvements are sustained through their ongoing conversations in the days and months after the workshop.

Results
In the big plant where I was the manager, the people improved their safety culture and cut the injury rate by 97% and increased earnings by 300%. We have seen similar changes in companies where we have conducted these workshops.
Conclusion
In highly functional organizations, safety, along with everything else, gets a lot better.
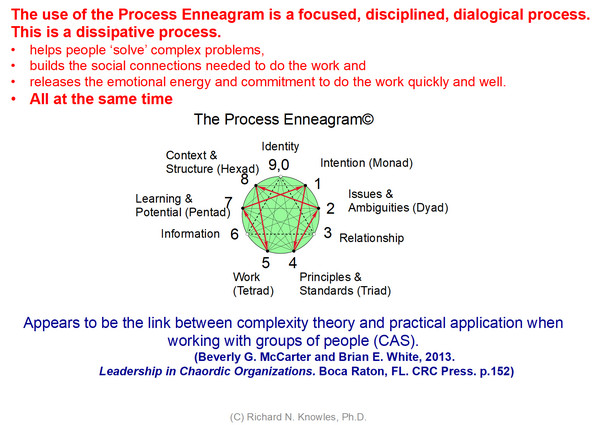
A lot of leaders are looking for the silver bullet to be able to lead in all situations, and to especially make needed safety improvements and to effect extraordinary change. There is a way: it is a framework we teach (Process Enneagram), which works because it is highly principle-based and partner-centered. And, because it is a tool for dealing with complex situations and multiple variables.









 Learning to work more effectively, through our safety work, spread to the whole organization. Each of you reading this newsletter can make a big difference as you engage with the people in your organizations, sharing information, building respect and trust. The impact of your work will spread.
Learning to work more effectively, through our safety work, spread to the whole organization. Each of you reading this newsletter can make a big difference as you engage with the people in your organizations, sharing information, building respect and trust. The impact of your work will spread. In this story, a wicked witch puts the princess and the whole kingdom to sleep for 100 years. They all have to wait for the arrival of the prince to kiss the princess and awaken everyone. As children, we all knew this story, but in this new book, Stephen Capizzano shifts the story to thinking about what happens in our organizations.
In this story, a wicked witch puts the princess and the whole kingdom to sleep for 100 years. They all have to wait for the arrival of the prince to kiss the princess and awaken everyone. As children, we all knew this story, but in this new book, Stephen Capizzano shifts the story to thinking about what happens in our organizations. When we were able to shed our old habits at our Plant in West Virginia, injury rates dropped by 97%, emissions to air, ground and water as reported to the EPA dropped 95%, productivity rose by 45% and earnings rose by 300%. As I walked the plant for 5 hours each day we were reminding ourselves to shed the old habits and create a much brighter future.
When we were able to shed our old habits at our Plant in West Virginia, injury rates dropped by 97%, emissions to air, ground and water as reported to the EPA dropped 95%, productivity rose by 45% and earnings rose by 300%. As I walked the plant for 5 hours each day we were reminding ourselves to shed the old habits and create a much brighter future.



